The ABC Diet Rules provide a comprehensive and effective approach to weight loss and improved health. This evidence-based diet focuses on balancing macronutrients, promoting nutrient-rich foods, and encouraging regular exercise.
With its structured meal plan, the ABC Diet eliminates guesswork and sets you on a path to success. By following these guidelines, you can lose weight, improve your blood sugar control, reduce inflammation, and boost your overall well-being.
General Overview of the ABC Diet Rules
The ABC Diet is a weight loss plan that involves alternating between three phases: the Attack, Cruise, and Balance phases. The Attack phase is a two-week period during which dieters consume primarily protein and vegetables. The Cruise phase is a longer period during which dieters gradually add more carbohydrates and fats to their diet.
The Balance phase is a maintenance phase during which dieters can eat a wider variety of foods but still need to follow some of the principles of the Attack and Cruise phases.
History and Context, Abc diet rules
The ABC Diet was created by Dr. Michel Montignac, a French physician, in the 1980s. Montignac believed that the key to weight loss was to control insulin levels. He developed the ABC Diet to help people lose weight by eating foods that have a low glycemic index (GI).
The GI is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, which helps to keep insulin levels stable. Insulin is a hormone that promotes fat storage, so by keeping insulin levels low, the ABC Diet helps to promote weight loss.
Dietary Restrictions and Allowances
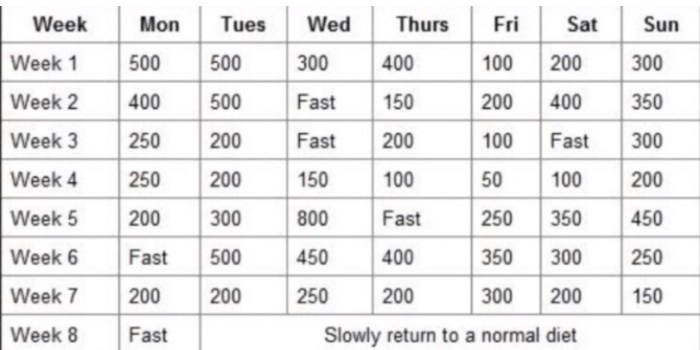
The ABC Diet strictly restricts certain food groups while allowing others. These restrictions are based on the belief that certain foods can cause inflammation and weight gain, while others promote satiety and weight loss.
The diet is divided into three phases, each with its own set of dietary guidelines. In general, the following foods are permitted on the ABC Diet:
Allowed Foods
- Fruits:Berries, apples, bananas, oranges, grapes, etc.
- Vegetables:Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, celery, etc.
- Lean protein:Chicken, fish, tofu, beans, lentils, etc.
- Whole grains:Brown rice, quinoa, oatmeal, etc.
- Healthy fats:Olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds, etc.
The following foods are prohibited on the ABC Diet:
Prohibited Foods
- Processed foods:Chips, cookies, candy, etc.
- Sugary drinks:Soda, juice, energy drinks, etc.
- Unhealthy fats:Saturated and trans fats, found in fatty meats, fried foods, etc.
- Refined carbohydrates:White bread, pasta, rice, etc.
- Alcohol:Beer, wine, spirits, etc.
The rationale behind these dietary restrictions is that processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can contribute to inflammation and weight gain. Refined carbohydrates can cause blood sugar spikes, leading to hunger and cravings. Alcohol can dehydrate the body and interfere with weight loss.
Meal Planning and Portion Control
The ABC Diet emphasizes a structured meal plan that rotates food groups over a four-day cycle. This plan includes:* Day 1 (A):Fruits and vegetables
Day 2 (B)
Lean protein and vegetables
Day 3 (C)
Carbohydrates and vegetables
Day 4
Repeat Day 1 Portion Sizes and Meal FrequencyPortion sizes on the ABC Diet are generally smaller than typical serving recommendations. The diet recommends consuming:* 1/2 cup of fruits and vegetables
- 3-4 ounces of lean protein
- 1/2 cup of cooked carbohydrates
- 2-3 snacks per day
Meal frequency should be spread out throughout the day, with meals eaten every 3-4 hours. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent overeating. Meal Preparation and PlanningTo make meal planning easier, consider:* Meal prepping:Prepare meals in advance to save time and ensure you have healthy options available.
Choosing nutrient-rich foods
Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Cooking at home
Becoming a pescetarian is an excellent choice for those seeking to reduce their meat consumption while still enjoying the benefits of seafood. By following a pescetarian diet, you’ll consume a variety of plant-based foods along with fish and other seafood.
If you’re interested in learning more about this dietary approach, be sure to check out our comprehensive guide on how to be a pescetarian. Our guide provides detailed information on the benefits, food choices, and lifestyle changes associated with this healthy eating pattern.
This gives you more control over ingredients and portion sizes.
Reading food labels
Pay attention to serving sizes and calorie content to avoid overeating.
Exercise Recommendations

Exercise plays a crucial role in the ABC Diet, complementing the dietary restrictions and portion control. Engaging in regular physical activity helps maximize weight loss results and promotes overall health and well-being.
Exercise Guidelines
The ABC Diet recommends a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Moderate-intensity exercises include brisk walking, cycling, and swimming, while vigorous-intensity exercises involve running, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and sprinting.
Benefits of Exercise
In conjunction with the ABC Diet, exercise provides numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Calorie Expenditure:Exercise helps burn calories, contributing to weight loss and maintenance.
- Boosted Metabolism:Regular exercise increases metabolism, helping the body burn more calories even at rest.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity:Exercise enhances the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, regulating blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:Exercise helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
- Enhanced Mood and Energy Levels:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting and energizing effects.
Incorporating regular exercise into the ABC Diet is essential for achieving optimal weight loss results and improving overall health and well-being.
Supplements and Hydration
The ABC Diet recommends the use of specific supplements to support weight loss and overall health. These include:
- Chromium picolinate:Helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce cravings.
- Green tea extract:Contains antioxidants and may boost metabolism.
- Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA):Supports fat loss and muscle gain.
Adequate hydration is crucial for overall health and weight management. It helps suppress appetite, improve metabolism, and flush out toxins. Aim for eight to ten glasses of water per day, or more if you are exercising or living in a hot climate.
Recommended Fluid Intake
The recommended daily fluid intake varies depending on factors such as activity level, climate, and overall health. However, a good rule of thumb is to drink half an ounce to one ounce of fluid for every pound of body weight per day.
Potential Benefits and Risks
The ABC Diet offers certain potential benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation. However, it also poses potential risks and side effects, such as nutrient deficiencies, digestive issues, and electrolyte imbalances.
Potential Benefits
- Weight loss:The ABC Diet restricts calorie intake, which can lead to weight loss.
- Improved blood sugar control:The diet emphasizes low-carbohydrate intake, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Reduced inflammation:Some studies suggest that the ABC Diet may help reduce inflammation in the body.
Potential Risks
- Nutrient deficiencies:The ABC Diet can be restrictive, which may lead to nutrient deficiencies if not followed carefully.
- Digestive issues:The high intake of fiber and protein in the ABC Diet can cause digestive issues, such as constipation or diarrhea.
- Electrolyte imbalances:The ABC Diet can cause electrolyte imbalances, especially if followed for an extended period.
Long-Term Sustainability and Maintenance: Abc Diet Rules
Sustaining the ABC Diet long-term can be challenging due to its restrictive nature. Gradual transition to a balanced eating plan is crucial to avoid nutrient deficiencies and maintain weight loss. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and mindful eating, are essential for sustainable weight management.
Strategies for Gradual Transition
- Gradually reintroduce food groups, starting with fruits and vegetables.
- Increase portion sizes slowly while monitoring calorie intake.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to promote satiety.
- Consult with a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Importance of Lifestyle Changes
Long-term weight management requires sustainable lifestyle changes beyond restrictive diets.
- Regular Exercise:Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Mindful Eating:Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, eat slowly, and avoid distractions while eating.
- Sleep:Get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to regulate hormones that affect appetite.
- Stress Management:Find healthy ways to cope with stress, as it can trigger overeating.
Variations and Modifications

The ABC Diet has several variations and modifications to cater to different individual needs and preferences.
One variation is the “modified ABC Diet,” which allows for greater flexibility in meal choices. This variation includes a wider range of protein sources, such as lean meats, poultry, and fish, and allows for more variety in vegetable and fruit consumption.
Rationale for Variations
The rationale behind these variations is to address the potential drawbacks of the original ABC Diet, such as its restrictiveness and lack of variety. By allowing for more flexibility and choice, the modified ABC Diet aims to make it more sustainable and enjoyable for individuals.
Choosing the Appropriate Variation
The choice of which variation to follow depends on individual needs and preferences. For those who prefer a more structured approach, the original ABC Diet may be suitable. For those who desire greater flexibility and variety, the modified ABC Diet may be a better option.
Additional Considerations
To enhance the effectiveness of the ABC Diet, individuals should consider various lifestyle factors that can impact their overall health and well-being.
Sleep, stress management, and other lifestyle choices play a crucial role in achieving optimal results with the ABC Diet.
Sleep
Getting adequate sleep is essential for overall health, including weight management. Sleep deprivation can lead to hormonal imbalances that increase hunger and cravings.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Establish a regular sleep-wake cycle, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to promote restful sleep.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to overeating and unhealthy food choices. Managing stress effectively can help individuals stay on track with their diet.
Embracing a pescetarian lifestyle can be a rewarding step towards a healthier and more sustainable diet. Whether you’re curious about reducing your meat consumption or seeking an alternative to vegetarianism, understanding how to be a pescetarian is essential. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the pescetarian diet, including its potential health benefits, dietary guidelines, and tips for making the transition.
- Engage in regular exercise, which is a natural stress reliever.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Seek support from friends, family, or a therapist if needed.
Other Lifestyle Factors
In addition to sleep and stress management, other lifestyle factors can contribute to the success of the ABC Diet:
- Regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support metabolism and reduce cravings.
- Mindful eating: Pay attention to hunger cues and eat slowly to avoid overeating.
Addressing Challenges and Setbacks
Following any diet can come with challenges and setbacks. Here are some tips for addressing them:
- Identify triggers: Determine what situations or emotions lead to unhealthy eating.
- Plan ahead: Prepare healthy snacks and meals to avoid temptation.
- Seek support: Join a support group or connect with a registered dietitian for guidance.
- Don’t give up: Remember that setbacks are part of the journey and don’t let them derail your progress.
Success Stories
Numerous individuals have experienced positive results following the ABC Diet. Here are a few success stories:
- “I lost 20 pounds in 12 weeks and have kept it off for over a year. The ABC Diet helped me change my relationship with food.” – Sarah, age 35
- “I feel so much better physically and mentally since starting the ABC Diet. My energy levels are up, and I’m sleeping better.” – John, age 42
End of Discussion
Whether you’re a seasoned dieter or just starting your weight loss journey, the ABC Diet Rules offer a practical and sustainable solution. Embrace these principles, make gradual lifestyle changes, and unlock the transformative power of healthy eating and exercise.
FAQ Compilation
Is the ABC Diet safe for everyone?
The ABC Diet is generally safe for most people, but it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
How much weight can I lose on the ABC Diet?
Weight loss varies depending on individual factors, but following the ABC Diet Rules consistently can lead to significant weight loss.
Is the ABC Diet a long-term solution for weight management?
Yes, the ABC Diet promotes sustainable eating habits and lifestyle changes that can support long-term weight management.